Leukaemia is a type of cancer that effects blood and its components. Once the marrow cell undergoes a leukaemia change, the leukaemia cells may grow and survive better than normal cells. Over time, the leukaemia cells crowd out or suppress the development of normal cells.The rate at which leukaemia progresses is different with each type of leukaemia. Leukaemia can broadly be divided into rapidly growing or acute leukaemia and more indolent, chronic leukaemia. A proper knowledge about this disease is essential as it helps patients and his care givers to cope better with this disease. After diagnosis and treatment, a large number of people with leukaemia live many good, quality years.
It is a rapidly growing blood cancer which requires urgent management. Treatment of ALL has undergone a sea change in last 30 years, from a certain death in few days in 1940s to about 80-90% chance of cure now, treatment of ALL has improved remarkably over the years.There are few important things to know about this disease
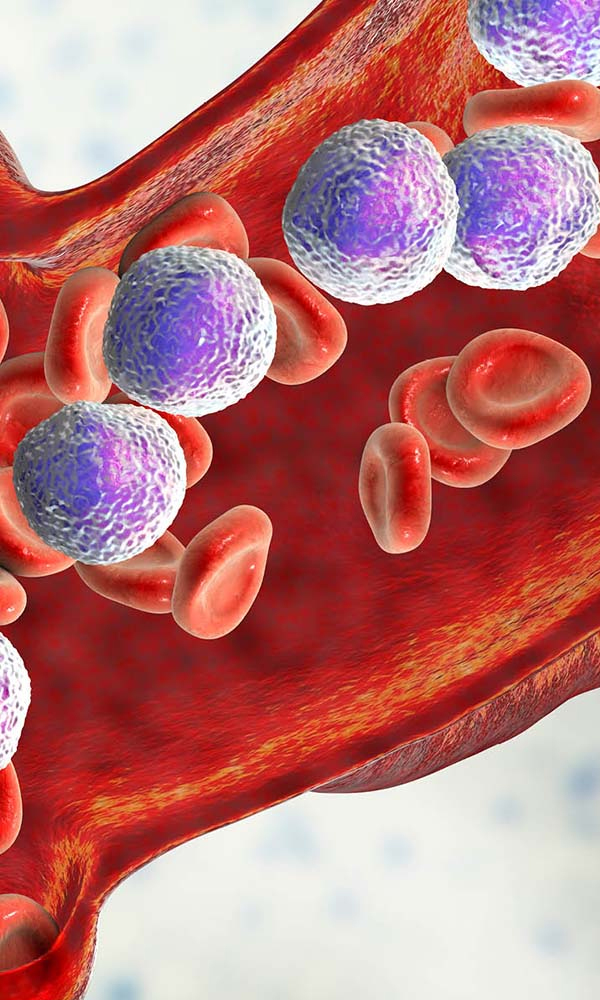
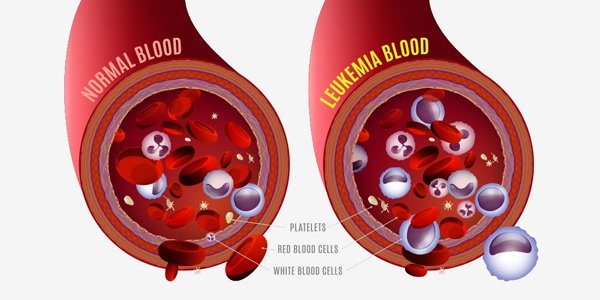
Symptoms are usually due to replacement of normal blood cells by abnormal ' blast ' cells
Patients with ALL require treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis because of fast disease progression. Treatment approach depends upon individual ' s subtype, risk factors, any infection at the time of diagnosis. Generally treatment can last between one and a half to three years. Treatment plan involves either of following options :
ALL is most aggressive of all blood cancers and can be a difficult disease to treat. Active research is going on in clinical trials to study new approaches to treat this devastating disease. For most people who have AML, as with other cancers, there are no obvious risk factors as to why they developed this disease. Patient should start treatment as soon as possible in a centre experienced in treating acute leukaemia.
The signs and symptoms of AML are common to other, less serious illness. There is usually a short history of 5-7 days before symptoms become more severe. Symptoms resemble those mentioned above for ALL except that lymph node, spleen, liver enlargement is less common and bleeding , fever is more prominent. In addition AML can present as mass of tumour cell in any part of body (myeloid sarcoma).
Most AML patients, particularly patients with high WBC counts, need treatment soon after diagnosis because of rapid disease progression. After diagnosis, initial aim is to get disease under control or in remission. Long term goal is to cure the disease.
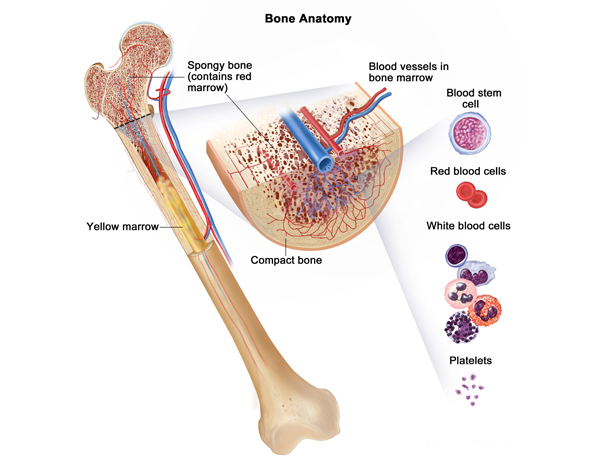
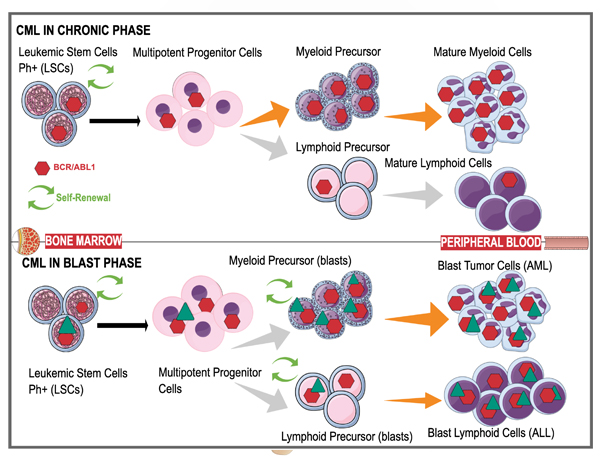
In contrast to acute leukaemia mentioned above, chronic leukaemia are more indolent and slow growing. CML is the most common type of leukaemia in India. CML when it was discovered, was untreatable and resulted in death in few months to years. However with a new drug called as imatinib these patients have almost normal life span .
Symptoms can be follows :
Treatment is with tablet imatinib, which has to be taken life long.
CLL is the most common leukemia of the west and second most common in India. It is usually diagnosed on routine blood test (CBC) in otherwise healthy patient, where there is increase in a specific type of cell(Lymphocyte). Most of the CLL patients do not require treatment, which is initiated only when CLL becomes symptomatic.
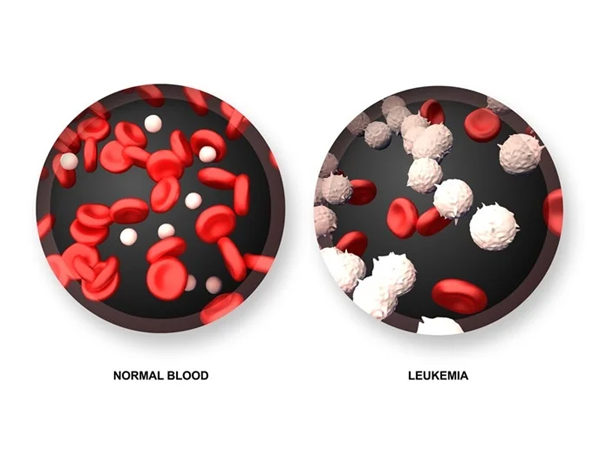
Numerous advances have been made in the field of hematology that have significantly improved the lives of patients with hematologic disorders. In the last 50 years alone, substantial strides have been made in the research, treatment, and prevention of blood diseases. Listed here are just a few, but those not mentioned are no less important. As past experience has shown us, even some of the most basic research taking place today has the potential to lead to promising life-saving treatments in the future.